Simulation Tool for Delta Robot Manipulation
Written on March 19th, 2017 by Elton Cheng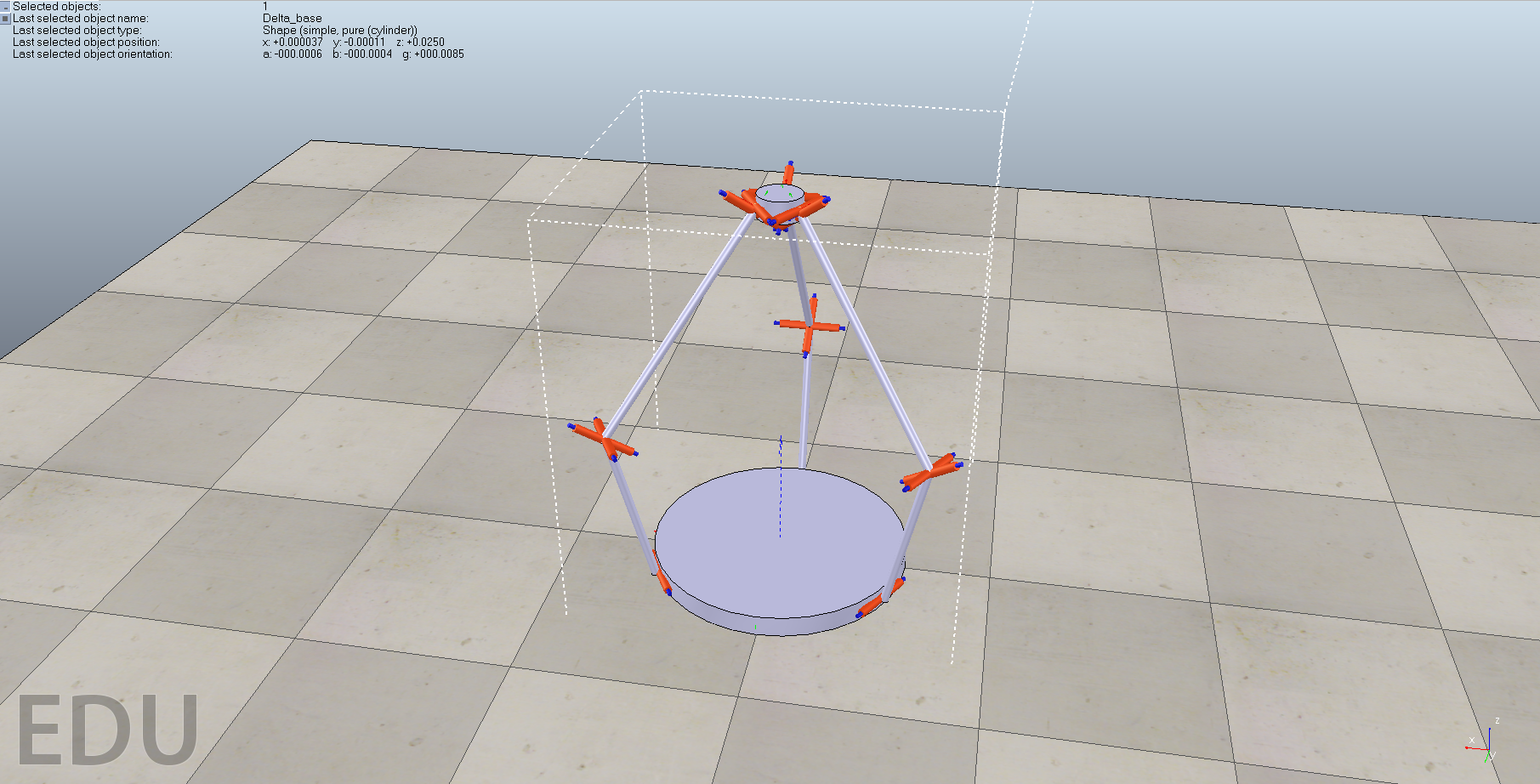
MSR Winter Project
Overview
In collaboration with the NxR lab, ME398 Senior Design team, and MS in Mechanical Engineering students, the goal for this portion of the project was to develop a simulation tool for a system that allows 3 or more mobile manipulators to cooperatively position a large-scale manufacturing component.
The parts that make up this part of the project are: the design of the mobile manipulators and control of the active joints of the robot.
Design of Mobile Manipulators
The design requirements for this project require the large component to be manipulatable in the xyz plane and roll-pitch-yaw rotations, as well as have some compliance in the xyz plane. Compliance is necessary to account for small errors in the trajectory and motion of the large object, as well as add an extra level of safety to this system.
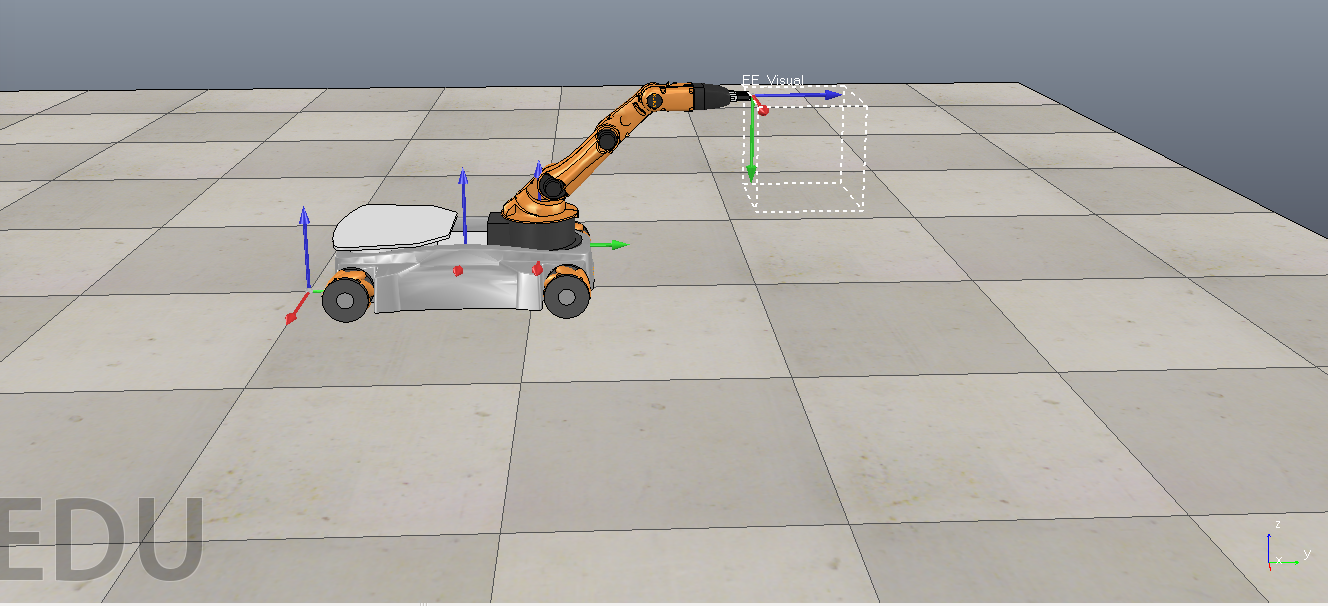
As a result of this, the robot consists of 4 major components: a mobile base, an active xyz platform that will allow movement in the xyz plane, a passive inverted delta robot that allows for compliance in the xyz plane, and a gimbal that allows for the robot to detect the orientation of the large object. The current status of this project is the development of the passive inverted delta robot and is the current focus for this simulation tool.
Multiple iterations for the design of this robot were discussed throughout the quarter. The model presented in this project is the current model. Scenes of the previous and current models can be found at this link.
Control of the Robot
V-REP was used as the current platform for simulating the inverted delta robot, due to its ability to create a closed-loop robot, simulate its dynamics, variety of built-in tools to assist in with this project, and cross-platform compatibility. ROS was used to interface with V-REP, through the RosInterface built-in plug-in, to control the joints of the delta robot and thus the position of the end effector.
Below are some videos of ROS python scripts publishing out joint states that V-REP subscribes to to control the robot. Source code for these scripts can be found here.
Status of the Project
3/18/17: I am currently looking into adding in inverse/forward kinematics code of the delta robot, which will allow trajectory control of the robot. Also, due to how the robot is currently modelled in V-REP, inverse kinematics calculations are not easy to obtain due to all the offsets the model contains. Because of this, I am working on improving this model that will allow easier calculations, as well as making it more flexible in design parameters (length of links, radius of base, etc).
3/27/17: Finished creating a V-REP scene, delta_robot_create_model.ttt, that would allow for customization of the inverted delta robot. Makes it much easier for customization and for future simulations. Will now be working on improving trajectory control, using this model.
5/25/17: Control of the simulation works. I am able to have the end effector move in a desired trajectory (video shown below), as well as take in input from a PS3 controller. With this set up, I now have a structure of code that I can use to port over to the physical hardware when the time comes.